Effective Naturopathy Cancer Treatment Consult Dr BRC Clinic >>
For Consulting Treatment Most Effectively without Adverse Side Effects, Naturally Click the Consult Link Above
Knowing Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (chemotherapy) refers to chemical drug therapy,
which refers to a treatment method that uses cytotoxic drugs to kill tumor
cells. Chemotherapy, together with surgery and radiotherapy, was known as one
of the three traditional cancer treatments in the past. Now with the rise of
targeted therapy and immunotherapy, the status of chemotherapy is not as
important as in the past, but it is still the cornerstone of tumor treatment.
Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment-based method, mainly
through intravenous administration, but also by oral route, or by thoracic or
abdominal perfusion. In some types of cancer, such as germ cell tumors,
chemotherapy alone is often curative. In many other malignant tumors that
cannot be cured by chemotherapy, the metastatic stage has already occurred.
Chemotherapy is still one of the main treatment methods for cancer, which can
greatly control the tumor progression and prolong the survival of patients. Of
course, chemotherapy will inevitably have some toxic and side effects, so it
must be administered to patients by doctors specialized in oncology.
When was chemotherapy started and by who?
Chemotherapy inventor Paul Ehrlich Started in 1911.
|
Table of Contents |
|
1. Origin 2. Ways 3. Principles of medication 4. Notes 5. Reasons for Failure 6. Main Impact 7. Whether or not to do chemotherapy? 8. Does Chemotherapy Work?
|
What is the Origin of Chemotherapy?
The term chemotherapy was first used by Paul Ehrlich,
director of the Institute for Infectious Diseases and Serum Research.
In Liverpool, a synthetic arsenic compound has been tried to
treat parasitic infections. But when Enlich tried to replicate the results, he
found that the disease developed resistance to the drug. He asked chemists to
try to synthesize many different arsenic compounds.
Later, in 1905, another German scientist, Fritz Schöding,
discovered the microorganism that causes syphilis, a sexually transmitted
disease. Enlich used his compounds to test therapeutics against the new
microbe. He was pleased to find that compound 606 worked. He called the
compound salflusan and dubbed it the "magic bullet" because of its
special effects on syphilis. It was first used in the treatment of syphilis in
1911.
Since then, scientists have been looking for chemicals that
can kill tumor cells without causing serious harm to the body. Scientists have
to test thousands of chemicals before finding effective ones.
Many types of cancer can be cured. Interferons are proteins
naturally produced by the body in response to certain viruses. They stimulate
the body's own defense system and kill some cancer cells. They have been used
successfully to treat certain types of leukemia and to slow the development of
some tumors.
What are the ways to perform Chemotherapy?
There are four ways of clinical application of chemotherapy:
1. Systemic chemotherapy for advanced or disseminated tumors
Because other effective treatments are often lacking for
patients with these tumors, chemotherapy is often used initially with the aim
of achieving remission in the near term. This chemotherapy is usually called
induction chemotherapy (Induction Chemotherapy). If the initial chemotherapy
regimen fails, switching to other chemotherapy regimens is called Salvage
Treatment.
2. Adjuvant Chemotherapy
It refers to chemotherapy after local treatment (surgery or
radiotherapy) to prevent the recurrence and metastasis of micrometastatic
lesions that may exist. For example, postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy in
patients with osteosarcoma, testicular tumors and high-risk breast cancer can
significantly improve the curative effect and improve the survival rate or
disease-free survival rate.
3. Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
For tumors that are relatively limited in clinical, but difficult to remove by surgery or radiotherapy, chemotherapy can be used before surgery or radiotherapy.
Its purpose is to hope that the tumor will shrink after chemotherapy, thereby reducing the scope of resection and reducing the disability caused by surgery.
Secondly, chemotherapy can inhibit or eliminate
possible micrometastases and improve the survival rate of patients.
It has been proved that neoadjuvant chemotherapy can reduce
the scope of surgery for bladder cancer, breast cancer, laryngeal cancer,
osteosarcoma and soft tissue sarcoma, non-small cell lung cancer, esophageal
cancer and head and neck cancer, or treat unresectable tumors after
chemotherapy. become a resectable tumor.
4. Special route Chemotherapy
(1) This is applicable in Endovascular treatment, including cancerous
intrathoracic, intraperitoneal and intrapericardial effusions. Usually
chemotherapy drugs (such as mitomycin, cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil, bleomycin)
are dissolved or diluted with an appropriate amount of fluid, and then injected
into the body cavity of various lesions through a drainage catheter, so as to
control malignant purpose of body cavity effusion.
(2) Intraspinal chemotherapy Leukemia and many solid tumors can invade the central nervous system, especially the meninges are the most vulnerable.
The treatment method is usually intrathecal administration by lumbar puncture, so that there is a higher drug concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid, so as to achieve the purpose of treatment.
Commonly used drugs in the
spinal canal are methotrexate and cytarabine.
(3) Arterial intubation chemotherapy, such as external
carotid artery branch intubation in the treatment of head and neck cancer,
hepatic artery intubation in the treatment of primary liver cancer or liver
metastases.
Selection and Application of Principles of Chemotherapy Medication
Although there are more than 40 kinds of commonly used anti-tumor drugs, and new drugs are still being developed, in order to achieve good curative effect, there must be a reasonable treatment plan. This includes the timing of medication, the selection and compatibility of drugs, and the order of administration, dose, course of treatment and interval time, etc.
In order
to achieve a comprehensive, reasonable and effective selection of combined
chemotherapy regimens is necessary.
In general, the composition of the combination chemotherapy
regimen should consider the following principles:
1. Use of drugs with different mechanisms of action in order
to act synergistically
2. Drugs should not have similar toxicity, so as not to add
to the toxicity and the patient cannot tolerate it
3. A single drug must be effective
Notes
(1) The diagnosis must be clear before starting treatment.
Leukemia, multiple myeloma and malignant histiocytoma must be diagnosed by
hematology and bone marrow cytology. Malignant lymphoma and various other solid
tumors must be pathologically diagnosed by local tissue.
Chemotherapy drugs are generally not used for diagnostic
treatment, let alone as a placebo, so as to avoid unnecessary losses to
patients.
(2) The patient's general condition is good, and the blood
picture and liver and kidney function are normal, so they can tolerate
chemotherapy.
The type and dose of
the drug should be carefully considered in any of the following situations:
- Elderly and frail
- Previously received multiple chemotherapy or concurrent radiotherapy
- Abnormal liver and kidney function
- Obvious anemia
- WBC or platelet lower than normal value
- Malnutrition, significantly decreased plasma protein
- Tumor bone marrow metastasis
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Fever, infection or other symptoms Complications
- Cardiomyopathy, etc.
- Chronic pulmonary insufficiency
What are the reasons of failure Chemotherapy?
Failure reasons of Chemotherapy:
1. Patient side
Insufficiency of bone marrow and other vital organs (liver,
kidney, heart, lung, etc.), the general condition of the patient is too poor to
tolerate chemotherapy.
2. Oncology
Primary or secondary drug resistance; the proliferation rate
is low and there are more cells in the quiescent phase; the tumor burden is too
large, and the tumor cells are more than 1011.
3. Drugs
The selectivity is not strong, and the damage to the tumor
and normal tissue cells is not much different. It is ineffective or too
ineffective for G0 phase cells; it cannot act on the tumor cells in the
"refuge" such as cannot pass through the blood-brain barrier and
enter the brain. Its most efficient usage has not yet been found.
Main influence
Even if you feel unwell during treatment, you can often
recover quickly between sessions (during the pause in treatment), and you can
resume your daily activities when you feel better.
If you are taking chemotherapy pills at home, chemotherapy
will cause very little disruption to your daily life.
During the time of oral chemotherapy, you still depend on
your own mental state, go to work and participate in various social activities
as usual.
Some chemotherapy that requires intravenous injection can be
done in a hospital outpatient department, but some cases do require a period of
hospital stay, which requires more changes to your daily routine. But as long
as you explain to your employer why you need a vacation, I believe most
employers will understand.
For most patients undergoing chemotherapy, the occasional
alcoholic beverage will not affect the effectiveness of the treatment.
Whether or not to do chemotherapy?
In outpatient clinics or wards, doctors and patients often
need to communicate treatment plans. When it comes to chemotherapy, many
patients will be afraid or even refuse.
"Doctor, I don't want chemotherapy, chemotherapy will
only go faster!"
"Doctor, can you not do chemotherapy, anyway, it's not
cured, so don't suffer from this."
These reactions are either worried about the ineffectiveness
of chemotherapy, or worry that the side effects of chemotherapy are too large
to be worth the harm. It shows that patients have not yet established a correct
understanding of chemotherapy, and there is a situation of partial
generalization, which usually requires us to spend a lot of time and energy to
explain patiently.
With everyone holding the view of "life first", let's
talk about our objective understanding of tumor chemotherapy.
1. Is chemotherapy effective?
Chemotherapy (referred to as "chemotherapy") is one
of the earliest "troikas" (surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy) for
tumor treatment. In recent years, with the continuous emergence of new
treatment methods, such as targeted therapy, immunotherapy, cell biological
therapy, etc., the status of chemotherapy has been impacted to a certain
extent. However, chemotherapy is still one of the main effective methods for
the treatment of tumors.
Does Chemotherapy Work?
First, on the definition of effect, doctors and patients may have different understandings. If the desired effect of the patient is a cure (term, complete remission), then most of the existing tumor treatment methods cannot achieve the biological characteristics of malignant tumors. Even if the early tumor is surgically removed, there are still some Transfer occurs. In fact, the vast majority of chronic diseases in the world cannot be cured. Therefore, the blind pursuit of healing is unrealistic.
Controlling tumors as much as possible, delaying disease
progression, paying attention to the time and quality of survival with tumors,
and emphasizing "people-oriented, survival with tumors" are our reasonable
expectations.
Then, under this consensus, the efficacy of chemotherapy is certain. A few chemotherapy-sensitive tumors, such as testicular cancer, leukemia, and Hodgkin lymphoma, can be completely relieved by chemotherapy alone, with a five-year survival rate of over 85%.
For the vast majority of tumors, the purpose of chemotherapy is to stabilize or shrink the lesions, control tumor progression, and prolong life.
The specific effect of
chemotherapy for each individual will vary depending on the type of cancer,
dose, whether it is combined with drugs, and physical conditions, and needs to
be scientifically evaluated according to the actual situation. For example, the
evaluation of the efficacy of solid tumors, the most commonly used RECIST
criteria.
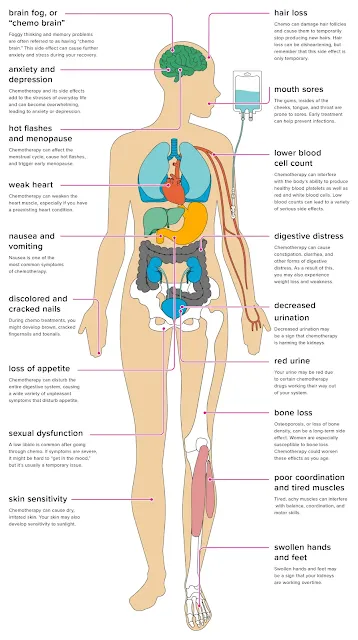
2. Are the side effects of chemotherapy great?
The earliest chemotherapy drug "nitrogen mustard" originated from the biochemical weapon "mustard gas" in war, and the modern arsenic trioxide is derived from the ancient "king of poisons" arsenic. It seems that chemotherapy is equivalent to taking poison, which is "chronic suicide". However, the purpose and mode of administration of the two are vastly different.
Although chemotherapy drugs kill tumor cells by mistake, they also accidentally injure normal tissue cells, but tumor cells are more vulnerable to attack. It is this "limited selectivity" feature of chemotherapy drugs that makes people love it and hate it.
Usually, chemotherapy is more likely to damage normal cells that are growing and dividing vigorously, such as gastrointestinal epithelial cells, bone marrow hematopoietic cells, hair follicles, etc., resulting in symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, hair loss, and cytopenias. However, these symptoms do not occur in everyone, and most of them are reversible. With the metabolism of the drug, the symptoms will gradually ease, and serious adverse reactions are only rare cases.
Importantly, there are also many drugs (including Chinese
herbal medicine) and methods that can relieve the corresponding symptoms in
clinical practice. Therefore, it is not necessary to give up chemotherapy just
for fear of adverse reactions.
3. Under what circumstances is chemotherapy suitable for use?
Chemotherapy is administered orally or intravenously, and the
drug is delivered to various organs of the body through the blood circulation,
thereby killing tumor cells. Unlike local treatments such as surgery and
radiotherapy, chemotherapy is a systemic method of administration. In theory,
chemotherapy is suitable as long as there are sensitive tumor cells in the
body. So, under what circumstances is chemotherapy appropriate?
1) Chemo-sensitive tumors, such as leukemia, multiple
myeloma, malignant lymphoma and other hematological tumors, chorioepithelial
carcinoma, testicular cancer, small cell lung cancer, etc., can be well
controlled by chemotherapy.
2) Adjuvant chemotherapy after surgical resection of solid
tumors and/or local radiotherapy, using chemotherapy to eliminate residual
tumor cells can reduce the probability of tumor metastasis, thereby prolonging
the life of patients.
3) The solid tumor has extensive or distant metastasis and is
not suitable for surgery or radiotherapy; if the solid tumor recurs after
surgery or after radiotherapy, chemotherapy can be used to stabilize or reduce
tumor lesions, control disease progression, and prolong survival.
4) Neoadjuvant chemotherapy before surgery, using
preoperative chemotherapy to shrink the lesions and increase the probability of
radical surgical resection.
Similarly, chemotherapy has corresponding contraindications, that is, those who are not expected to tolerate or benefit from chemotherapy:
i.) Elderly and frail, poor nutritional status, unable to
tolerate chemotherapy, and the expected survival time is less than 2 months.
ii.) Insufficiency of important organs, such as liver,
kidney, heart and lung, bone marrow hematopoietic function, etc. have more
serious dysfunction.
iii.) Those who have serious infectious diseases such as
chickenpox and herpes zoster, and those who are allergic to chemotherapy drugs.
iv.) For women who are pregnant and breastfeeding, most
chemotherapy drugs are contraindicated, and a few are used with caution.
v.) Psychiatric patients who cannot cooperate with treatment
4. How many times of chemotherapy do cancer patients need?
Since chemotherapy can destroy tumor cells, why can't chemotherapy be performed in one treatment, but in multiple cycles?
This is due
to the "limited selectivity" characteristic of chemotherapy. The
human body cannot withstand too many chemotherapy drugs at one time, and one
chemotherapy can only destroy a certain percentage of tumor cells. By dividing
the chemotherapy dose into multiple treatments in a multi-cycle manner, more
tumor cells can be eliminated without causing serious adverse reactions.
The frequency of chemotherapy is determined according to the specific condition of the patient (tumor location, pathological type, clinical stage, etc.). For example, 4 times of adjuvant chemotherapy is usually performed after surgery for early-stage tumors.
If postoperative pathology
shows high risk factors such as vascular tumor thrombus or nerve invasion or
lymph node metastasis, 6 or more times of chemotherapy are required.
For palliative chemotherapy, after 2 cycles of chemotherapy,
the efficacy will be evaluated by CT, MRI and other means. If it is effective,
chemotherapy will generally be continued; on the contrary, if it is
ineffective, the chemotherapy regimen will be changed according to the
guidelines, and post-treatment evaluation will be continued.
Understanding Chemotherapy under Conditions
Colds are one of the most common diseases we suffer from.
Some people have other diseases secondary to a cold, such as viral myocarditis,
bacterial tracheobronchitis, pneumonia and meningitis, and so on. This type of
disease is due to the changes in bodily functions after the body is invaded by
pathogenic organisms, and belongs to infectious diseases. Infectious diseases
and tumors are the first diseases caused by pathogens invading the body
The second type of disease, similar to the elderly often suffer from certain chronic diseases, such as coronary heart disease, diabetes and so on. People who love sports and outdoor activities often experience dehydration and heat stroke. This large category of diseases is caused by abnormal functions of the patient's body tissues and organs due to a variety of reasons. Such as organ function enhancement, the function is higher than the normal level, called hyperfunction. Organ function is weakened, and the function is lower than normal, which is called hypofunction. Representative diseases such as hypertension, hypotension, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism and so on.
The treatment of such diseases is carried out by exciting or inhibiting
the function of the corresponding system, organ or tissue of the body.
Therefore, the drug is directly aimed at the patient's body.
For the treatment of the first type of disease, because its cause is the infection of bacteria, viruses and other pathogenic organisms or the body produces tumor cells, the target of the treatment is not the patient's body, but the pathogen.
Chemotherapy is a general term for drug treatment of
all pathogens that cause diseases. Pathogens include viruses, bacteria, fungi,
parasites and tumor cells.
From this, we know that "chemotherapy" is a large class of drug treatment, which is the use of drugs to treat viral infections, bacterial infections, fungal infections, and parasitic infections, including the treatment of malignant tumors.
The scope of this concept is very broad, including but by no means limited to the treatment of anti-malignant tumors. So, let's not get scared when we hear about chemotherapy. Because we usually see chemical treatment everywhere, for example, if you suffer from athlete's foot, applying ointment for athlete's foot is performing chemical treatment. If you suffer from trachoma, chloramphenicol eye drops or erythromycin eye ointment for trachoma are also treated with chemotherapy.
Chemotherapeutic drugs (chemotherapy drugs)
All chemical
substances that have selective inhibitory or killing effects on invasive
pathogens, but have no or only mild toxic effects on the body (host).
There are many types of pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, mycoplasma, chlamydia, rickettsia, spirochetes, fungi, parasites and tumor cells.
Correspondingly, there are many types of chemotherapy drugs,
including antiviral drugs, antifungal drugs, antibacterial drugs, antiparasitic
drugs and anticancer drugs.
Infections with different pathogens should be treated with corresponding types of chemotherapy drugs. And in addition to empirical selection of drugs, it is best to choose according to the type of sensitive drugs after pathogen detection and drug susceptibility testing.
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most common pathogenic bacteria. It is ubiquitous in nature and can be found in the air, water, dust, and human and animal excrement.
This is E. coli, and the therapeutic E. coli infection is a zoonotic disease that often causes severe diarrhea and sepsis.
In addition to this, there are various parasites, which are roundworms in the intestines
This is a parasite carried by aquatic products
Top cause of death before Chemotherapy
Whether it is bacterial infection, viral infection, or parasitic infection, pathogenic organisms invade the body and cause disease. Before the invention of effective chemotherapeutic drugs, such diseases were the number one cause of death in humans. In addition, our body can also produce tumor cells.
When tumor cells escape the monitoring of the body's immune system
and multiply, it will endanger people's lives. Malignant tumors are the
diseases that cause the highest mortality rate in humans today. Therefore, for
infectious diseases, malignant tumors must be actively treated. Among them,
chemotherapy, that is, treatment with drugs, is a very important means.
Chemotherapy drugs are classified according to their effects:
antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal, antiparasitic and anticancer drugs. Among
them, there are many kinds of antibacterial drugs and the most used ones.
The scope of antibacterial treatment is not limited to bacterial infections. Some antibiotics are also used to treat chlamydia, mycoplasma, rickettsial infections and more.
There is also a special class of antibacterial drugs, called
anti-tuberculosis drugs, which are specially used to treat tuberculosis.
Chemotherapy drugs are complicated, and their use must be carried out under the guidance of a professional doctor.
Never take it for granted and use it indiscriminately by feeling, because the medicine is not symptomatic and may make the treatment ineffective and delay the disease.
If it is not used properly, it may develop drug-resistant bacteria for itself, and eventually become incurable.
Conclusion
In
conclusion, the formulation of the number of chemotherapy is not a
personal empirical decision of the doctor, but is based on the analysis
and summary of clinical trial data. In this regard, you can refer to the
CDC or FDA guidelines. Chemotherapy is the abbreviation of chemical drug therapy,
which is a treatment method that uses chemical drugs to prevent the
proliferation, infiltration, and metastasis of cancer cells, and finally kill
cancer cells. It is a systemic treatment, and together with surgery and
radiotherapy it is called the three major treatments for cancer.
Author's Bio
Education: MBBS, MD
Occupation: Medical Doctor
Specialization: Community Medicine, General Surgery, Natural Treatment
Experience: 18 Years as a Medical Practitioner



Comments
Post a Comment