What does Biotin (Vitamin H) stand for?
Biotin, also known as vitamin H and coenzyme R, is a
water-soluble vitamin and also belongs to the vitamin B family, B7. It is a
necessary substance for the synthesis of vitamin C and an indispensable
substance for the normal metabolism of fat and protein. It is a nutrient
necessary to maintain the natural growth, development and normal function of
the human body.
Biotin is one of the B vitamins, also known as vitamin H, vitamin B7, coenzyme R (Coenzyme R) and so on.
In the 1930s, when studying the
growth and respiration promoting factors of yeast growth factors and rhizobia,
it was discovered from the liver as a factor that can prevent hair loss and
skin damage in rats induced by feeding raw egg protein. Biotin is a member of
the water-soluble vitamin B group.
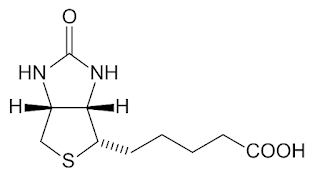
Biotin (Vitamin H) Structure
Biotin (vitamin H) refers to a parallel ring with urea and thiophene combined with a valeric acid side chain. Biotin is a B vitamin and is a water-soluble vitamin.
Biotin is a necessary substance for the synthesis of vitamin C and an indispensable substance for the normal metabolism of fat and protein.
Biotin is also a coenzyme of various carboxylases and acts as a CO2
carrier in the carboxylase reaction in vivo.
What type of substance is Biotin?
Biotin is a photosensitive substance that constitutes the photoreceptor cells, which can maintain the integrity and soundness of the epithelial tissue structure.
Is biotin helpful in body growth?
Biotin can also enhance the body's immune response
and resistance and maintain normal growth and development.
Biotin is helpful in treatment of which conditions?
Clinically, biotin is used for the treatment of
arteriosclerosis, stroke, abnormal lipid metabolism, hypertension, coronary
heart disease and blood circulation disorders.
Is biotin helpful in cosmetics?
In cosmetics, it can improve the circulation speed of blood
in the blood vessels of the skin. In the concentration range of 0.1% to 1.0%,
it is easy to mix with the oil in the formula.
It can be used in skin care vanishing cream, sports liquid, foot pain cream, shaving liquid, and shampoo.
What are the physiological functions of Biotin?
Biotin has a variety of physiological functions. It can help the normal synthesis and metabolism of fat, glycogen and amino acids in the human body, promote the normal operation and growth of sweat glands, nerve tissue, bone marrow, male gonads, skin and hair, reduce eczema, dermatitis symptoms, prevent white hair and hair loss, help to treat baldness, relieve muscle pain, promote urea synthesis and excretion, purine synthesis and oleic acid biosynthesis.
It is helpful to treat arteriosclerosis, stroke, abnormal lipid metabolism, hypertension, coronary
heart disease and blood circulation disorders.
What the scarcity of biotin lead to?
Lack of biotin can cause dermatitis, eczema, atrophic
glossitis, hyperesthesia, muscle pain, fatigue, anorexia and mild anemia, hair
loss.
Excessive biotin is generally not too toxic, and high-dose biotin treatment of seborrheic dermatitis has not found abnormal protein metabolism or genetic errors and other metabolic abnormalities.
What is the recommendable dose of biotin?
The recommended dosage for adults is 25 - 300 μg per day.
Since biotin only stays in the human body for 3 to 6 hours, it must be supplemented every day.
How id biotin useful?
Biotin is a coenzyme of various enzymes in the human body, which participates in the metabolism of fatty acids and carbohydrates in the body, promotes protein synthesis.
It also participates in the metabolism of vitamin B12, folic acid, and pantothenic acid.
It also promotes urea synthesis and excretion.
It helps the normal synthesis and metabolism of fat, glycogen and amino acids in the human body
2. Promote the normal operation and growth of sweat glands, nerve tissue, bone marrow, male gonads, skin and hair, and relieve symptoms of eczema and dermatitis
3. Prevent gray hair and hair loss, and help to treat baldness
4. Relieve muscle pain
5.
Promote
urea synthesis and excretion, purine synthesis and oleic acid biosynthesis
Is biotin a nutrient for fatty acid synthesis?
Biotin, also known as vitamin B7, is a member of the vitamin B group. It is mainly the cofactor of various carbonic enzymes in the human body.
It is an indispensable nutrient for fatty acid synthesis, glycogenesis, and amino acid decomposition. Energy is very important.
In addition, biotin has an excellent cosmetic effect and can
maintain strong hair, skin and nails. It is often added to beauty products and
can also be called vitamin H. H is the abbreviation of hair Haar and skin Haut
in German.
Which foods contain biotin?
Biotin comes from a wide variety of sources, including egg
yolks, beer, yeast, nuts, beans, whole grains, mushrooms, bananas, cauliflower,
fish, and more.
The raw protein contains an avidin called Avidin, which
inhibits the body's absorption rate.
What are the recommended proven efficacy (benefits) of biotin?
1. Improve hair loss (baldness)
Hair loss is a health concern for many people, related to
appearance and self-confidence, and it is estimated that nearly 50% of men and
women are affected by different patterns of hair loss.
Nutrient deficiencies are often associated with chronic
telogen effluvium, androgenetic alopecia, female pattern baldness, and patchy
alopecia. While biotin is good for hair growth and strong hair, one of the main
symptoms of deficiency is hair loss.
In one case study (in a formula-fed infant deficient in biotin), supplementation with biotin relieved symptoms of perioral dermatitis and patchyhairloss caused by the deficiency.
NB The effect of biotin on improving hair loss is unknown. So far, there is no complete clinical trial to confirm that additional supplementation can prevent or treat hair loss in the absence of deficiency.
2. Improve BrittleNails
Brittle nail disease is a structural abnormality of the nails. The main symptoms are loss of elasticity and softness of the nails, accompanied by cracking, peeling and crushing.
It is estimated that about 20%
of the population is affected by this disease, and the incidence of women is
more than men. 2 times.
Brittle nails are usually idiopathic (meaning the cause is
unknown) and may be caused by skin or systemic disease, nutritional
deficiencies, drug use, or trauma.
In animal medicine, biotin is often used to improve hoof
defects or abnormalities in ungulates such as horses, cattle and sheep.
Biotin supplementation has also been found to improve brittle
nails (63% to 91% of subjects reported improvement) and nail plate thickness in
several human studies.
The underlying mechanism is related to improving the
synthesis of lipid molecules required for the manufacture of nail plate
keratinocytes.
Biotin might have the effect of improving brittle nail disease, but due to the small scale of the sample study, more large-scale experiments with precise design are needed to confirm
3. improve diabetes
Diabetes is one of the oldest diseases in human history and
was first discovered in ancient Egypt 3,000 years ago.
The main causative factors of diabetes are related to genes
and life factors, such as lack of exercise, sedentary, smoking and drinking.
Among them, obesity accounts for about 55% and is the most common causative
factor.
A small study found that people with diabetes typically have
lower blood biotin concentrations than healthy people, and that supplementation
helped improve fasting blood sugar levels.
Another double-blind controlled study (90 days in 447
diabetic patients with poor glycemic control) showed that the additional use of
chromium and biotin resulted in better glycemic control (improvement of
glycation) than drug treatment alone. hemoglobin and fasting blood glucose).
The mechanism behind it is related to factors such as
biotin's promotion of glucose synthesis into fat, glucokinase secretion
(promoting hepatic glucose synthesis), and triggering of insulin, so it is
believed to help maintain blood sugar stability.
4. Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease caused by
progressive damage to the myelin sheath in the brain or spinal cord, which
coats nerve fibers, affecting other parts of the body.
Depending on the affected area, symptoms may include numbness
in the limbs, impaired vision, fatigue, slurred speech, and dizziness.
A preliminary small study suggests that high doses of biotin
help improve clinical symptoms of multiple sclerosis (slow progression and
disability).
Another double-blind controlled study (12 months in 154
patients with multiple sclerosis) also found that high-dose biotin (100 μg/tid)
reduced disability status compared with placebo Scale score (ExpandedDisabilityStatusScale)
and improved clinical impression.
The mechanism behind it is related to the following two
properties of biotin.
A. Activates carboxylase, promotes myelin repair (by
increasing fatty acid synthesis)
b. Protects axons from degeneration caused by hypoxia (by
increasing neuronal energy production)
High-dose biotin may help improve multiple
sclerosis, but more experiments are needed to confirm
Does biotin have any side effects?
Biotin is a very safe nutrient, safe in most cases without
side effects, and studies have used ultra-high doses of 100mg to 600mg for
several months with no adverse effects (due to its water-soluble properties,
excess is excreted in the urine).
Safety Precautions (Contraindications)
Concomitant use of high doses of pantothenic acid (vitamin
B5) may have a competitive effect and hinder the absorption of biotin.
Taking antibiotics or sulfonamide antibiotics
(Sulfonamideantibacterial) will destroy the good bacteria in the intestinal
tract, resulting in a decrease in the biotin synthesis rate.
Long-term use of antiepileptic drugs and anticonvulsants can
reduce the absorption and reabsorption of biotin in the intestinal and renal
tubules.
Is biotin deficiency common?
Because intestinal bacteria can produce biotin by themselves,
deficiency is rare. Most of the deficiency occurs in patients with congenital
anomalies or deficiency of biotinidase and carboxylase. Symptoms of deficiency
include eczema, hair loss and conjunctivitis. .
Biotin for Weight Loss
A Weight loss biotin is mainly to play a certain auxiliary role. At the same time, it must be combined with some exercise to achieve better results.
The main thing is to choose and apply some drugs that are
conducive to weight loss, such as weight loss capsules or weight loss.
products, etc. for conditioning treatment, but also need to cooperate with some
dietary conditioning
How effective is biotin for weight loss?
First of all, you have to know your physique. A Weight loss
biotin is mainly to play a certain auxiliary role. At the same time, it must be
combined with some exercise to achieve better results.
The main thing is to choose and apply some drugs that are
conducive to weight loss, such as weight loss capsules or weight loss.
products, etc. for conditioning treatment, but also need to cooperate with some
dietary conditioning
Conclusion
Biotin is a type of vitamin, also known as vitamin H, vitamin
B7, coenzyme R and so on. Biotin is a water-soluble vitamin, which is
relatively stable to heat and has little loss in general cooking. Biotin is a
coenzyme of many carboxylases in the body and plays an important role in the
metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, proteins and nucleic acids. Under normal
circumstances, adults with a balanced diet are generally not deficient in
biotin. The avidin in the raw egg white will affect the absorption of biotin.
After the egg white is cooked, the avidin is destroyed, and the biotin can be
reused and absorbed.
Name: Gwynneth May
Educational Qualification: MBBS, MD (Medicine) Gold Medalist
Profession: Doctor
Experience: 16 Years of Work Experience as a Medical Practitioner


Comments
Post a Comment